Pneumatic Conveying: A Unique approach to Maximizing Powder & Bulk Material Transfer
Pneumatic Conveying: A Unique approach to
Maximizing Powder & Bulk Material Transfer
Industrial material handling poses a constant challenge to the efficient and reliable transfer of powders and bulk materials. An innovative and flexible technology, pneumatic conveying is one of the most effective and efficient methods for conveying materials. This blog explores the intricacies of pneumatic conveying, highlighting its distinctive approach to maximizing the transfer of powders and bulk materials in various industries.

Understanding Pneumatic Conveying
Typically, moving bulk materials through a pipeline with the help of a gas, such as air or nitrogen, is known as pneumatic conveying. With precision and flexibility, pneumatic conveying can handle a wide range of materials, from fine powders to larger granular particles.
How does Pneumatic Conveying System Works?
The process involves several steps, and the specific configuration can vary based on the type of pneumatic conveying system (dilute phase, dense phase, or others) and the characteristics of the materials being conveyed. Here’s a general step-by-step explanation of how a pneumatic conveying system works:
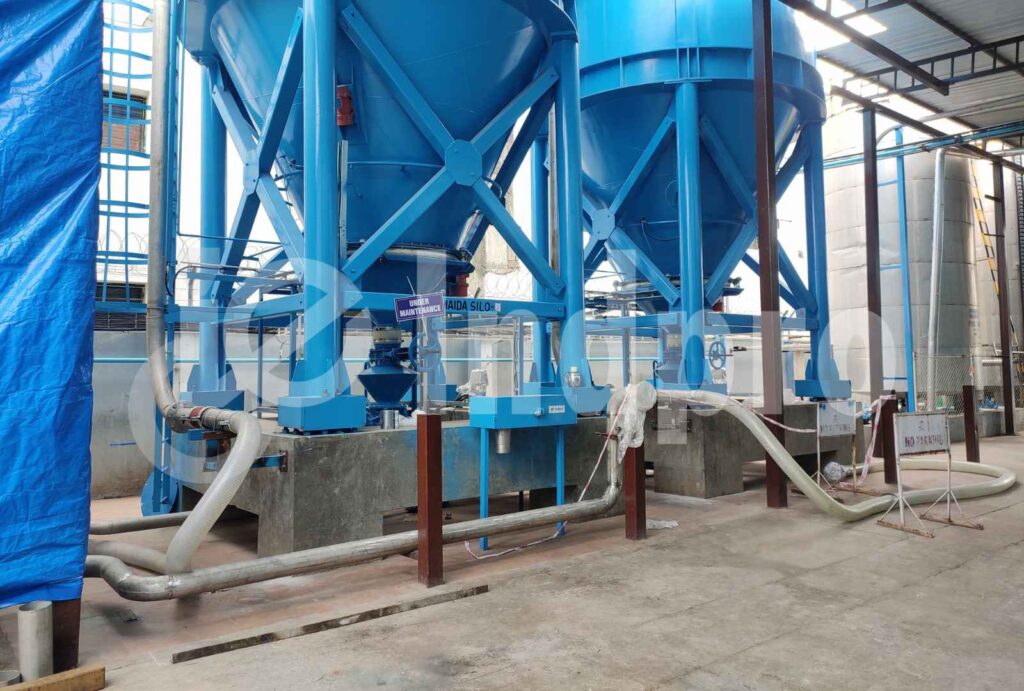
Step 1: Material Pickup
Typically, as the first step, bulk material is picked up from a storage silo or hopper. Several devices can be used to achieve this, including rotary valves, screw feeders, dense phase vessels, and venturi eductors, depending on the system’s design.

Step 2: Material introduced in Conveying Line
The material is passed into a conveying line, which is typically a pipeline or duct that connects the pickup point to the destination or receiving point. The conveying line is designed to transport the material using a controlled flow of air or gas.

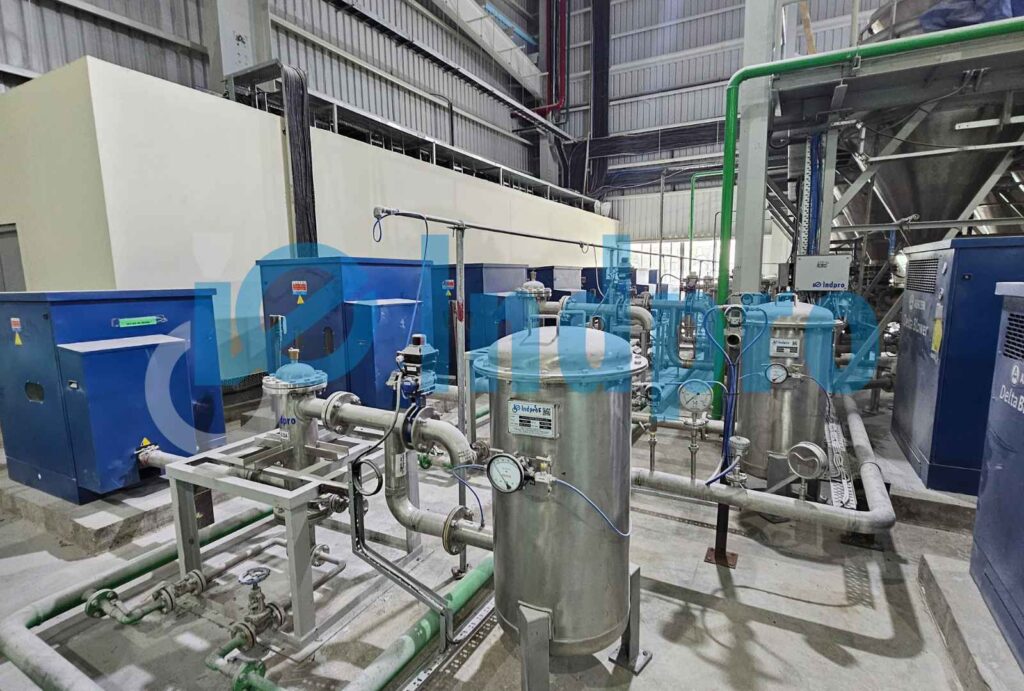
Step 3: Air or Gas Supply
Compressed air or another gas is supplied to the conveying line to create a flow that carries the material. The pressure and flow rate of the air or gas are controlled based on the design criteria of the conveying system.

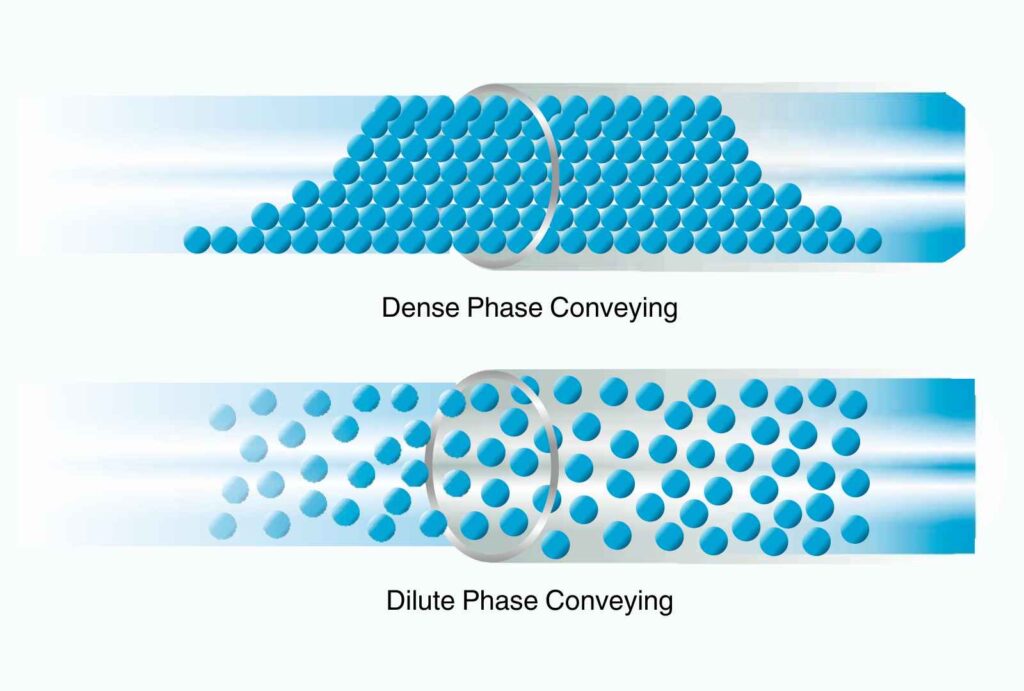
Step 4: Material Suspension (Dilute Phase) or Material Plug (Dense Phase)
Material is conveyed in a dilute phase pneumatic conveying as a low-density mixture of air that resembles fluid, also known as suspension flow. In dense phase pneumatic conveying, the material is conveyed as a dense plug or slug with a higher material-to-air ratio.
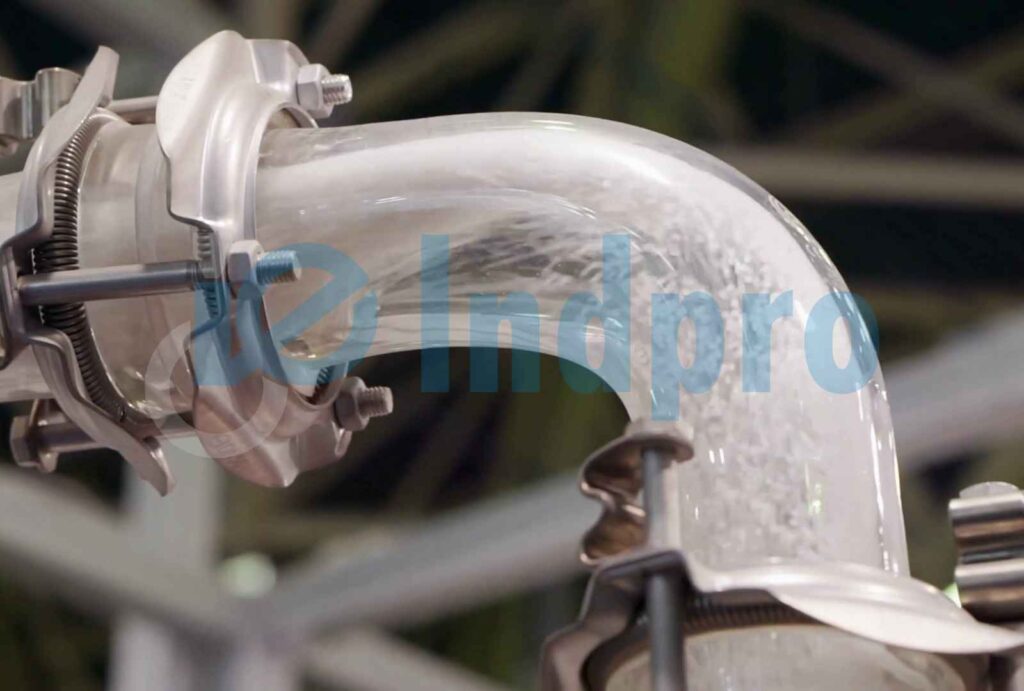
Step 5: Material Conveying
The material-air mixture travels through the conveying line, overcoming the effects of gravity and any resistance encountered in the pipeline. During this process, the material is moved by the force of moving air or gas.

Step 6: Air Material Separation
Near the destination point, the conveying air or gas is separated from the material. This can occur using various separation devices such as cyclones, filters, or other air-material separation equipment. The separated gas can be recycled back into the system to maintain the temperature, humidity or inert gas concentration.
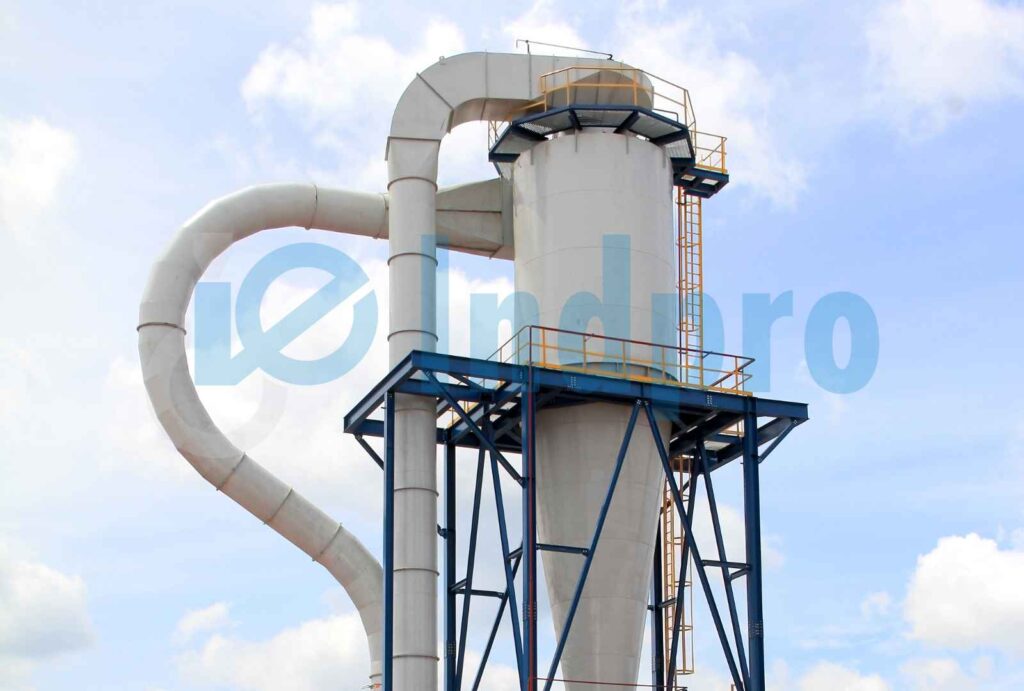

Step 7: Material Receiving
The conveyed material is discharged at the destination point, such as a storage vessel, reactor, mixer, or other processing equipment.
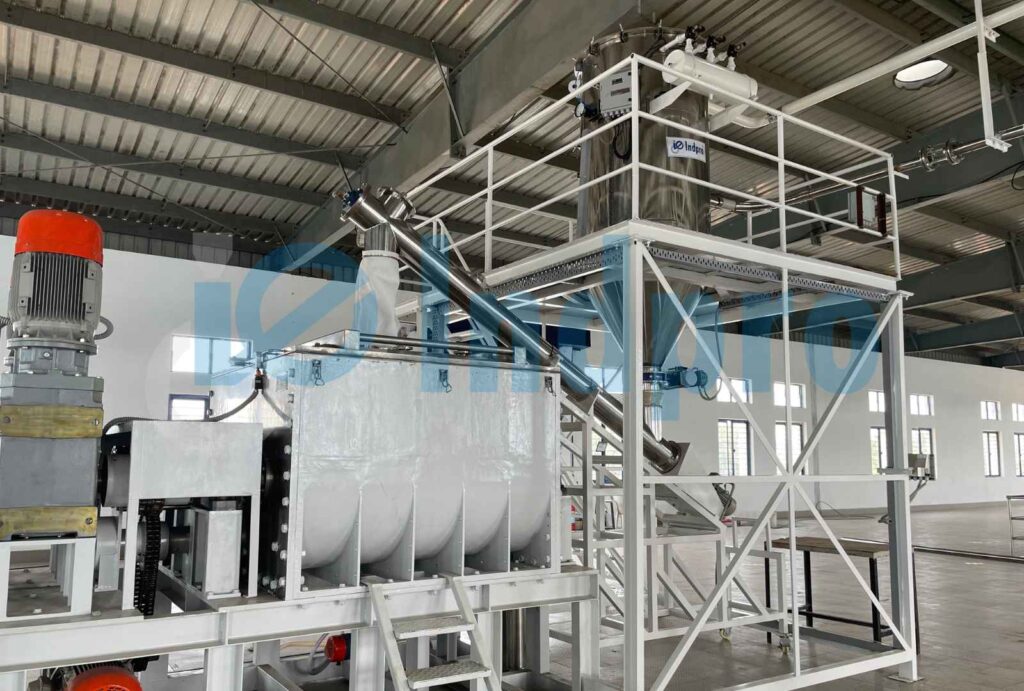

Step 8: Dust Collection (Optional)
In systems conveying dusty materials, dust collection equipment may be employed to capture and separate airborne particles from the conveying air, ensuring a clean and safe working environment.
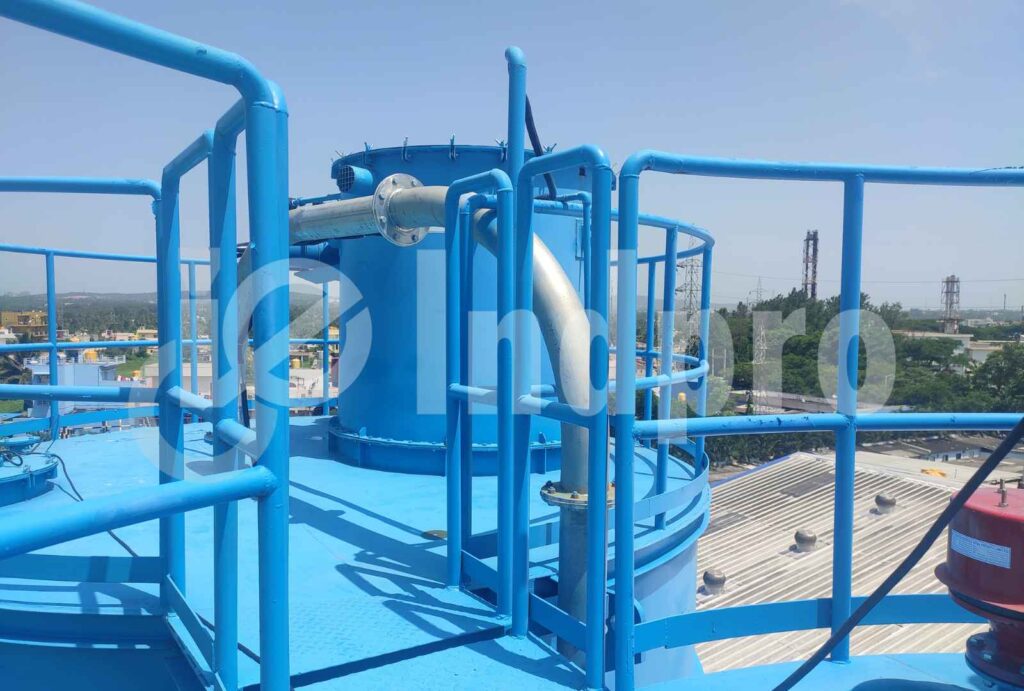

The entire pneumatic conveying process is controlled and monitored by a control system. This system regulates parameters such as air or gas flow, pressure, and material feed rates to ensure efficient and reliable operation. Sensors and instruments provide real-time feedback for monitoring and adjustments.
It’s important to note that the specific design and components of a pneumatic conveying system can vary based on factors such as the type of material, conveying distance, required flow rates, and the characteristics of the process. Proper system design and selection are essential for achieving optimal performance in pneumatic conveying applications.
How pneumatic conveying is maximizing efficiency in powder & bulk material transfer?
Pneumatic conveying process offers several advantages that contribute to its efficiency and effectiveness in material handling. Here are some benefits of pneumatic conveying that contributes to maximizing powder and bulk material transfer:
1. Efficient Material Transfer:
Pneumatic conveying systems enable efficient and rapid transfer of powder and bulk materials from one point to another at various desired capacities.
2. Reduced Material Degradation:
The gentle handling nature of dense phase pneumatic conveying minimizes material degradation during transfer. This is crucial for handling fragile or sensitive materials where maintaining product integrity is essential.
3. Clean and Enclosed Operation:
Pneumatic conveying systems operate in enclosed pipelines, minimizing the risk of contamination and ensuring a clean transfer process. This is particularly important in industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.
4. Versatility in Conveying Materials
Pneumatic conveying systems are capable of handling various powder and bulk materials, from fine powders and granules to pellets and abrasive substances, making them highly adaptable across different industries.
5. Flexibility in System Design:
The flexibility in design of pneumatic conveying systems allows them to be customized for various facility layouts, making it possible to convey materials over long distances or through complicated routes.
6. Reduced Manual Handling and Labor Costs:
Automation in pneumatic conveying reduces the need for manual labor in material loading, unloading, and transportation. This results in increased efficiency and improved workplace safety.
7. Space Efficiency:
The use of pneumatic conveying systems is often more space-efficient than the use of mechanical conveyor systems. A conveying system can navigate around existing equipment or within a limited amount of space in facilities where space is limited.
8. Energy Efficiency:
Modern pneumatic conveying systems are designed with energy efficiency in mind. Variable frequency drives (VFDs), efficient blower designs, and optimized control systems contribute to energy savings.
9. Integration with Process Automation:
Pneumatic conveying systems can be easily integrated into overall process automation. This allows for precise control, monitoring, and optimization of material flow, contributing to overall operational efficiency.
10. Reduced Environmental Impact:
Enclosed pneumatic conveying systems minimize dust emissions, contributing to a cleaner and safer working environment. The enclosed nature of these systems also prevents material spillage and waste.
11. Continuous and Reliable Operation:
Pneumatic conveying systems can operate continuously, ensuring a consistent flow of materials. Their reliability is further enhanced by features like automatic controls, monitoring systems, and preventive maintenance measures.
12. Material Quality Preservation:
The gentle conveying process helps preserve the quality of materials, preventing issues such as segregation, attrition, or contamination.
By combining these features, pneumatic conveying systems maximize the efficiency of powder and bulk material transfer, making them integral to numerous industries where reliable and contamination-free material handling is essential.



