Powder Handling Systems & Equipment: A Comprehensive Guide
Powder Handling Systems & Equipment: A Comprehensive Guide
Efficient powder handling is paramount for industries such as food processing, plastics, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and minerals. This blog delves into the key aspects of powder handling systems and equipment, their challenges, and the advanced technologies driving innovation in the field.

Why Powder Handling Matters
Powder handling systems are essential for industrial processes involving fine particulate materials. From ensuring consistency in food production to preventing hazards in chemical operations, these systems streamline operations and boost productivity. The primary objectives are:
- Contamination Prevention: Maintaining product purity and preventing cross-contamination.
- Flow Optimization: Ensuring smooth and efficient material flow to avoid blockages and downtime.
- Safety Assurance: Mitigating risks associated with dust explosions, inhalation hazards, and other safety concerns.
Challenges in Powder Handling
Handling powders presents unique challenges due to their physical properties and sensitivity to environmental conditions:
1. Dust Control and Containment: Powders generate fine dust during transfer, which can pose health hazards and increase the risk of explosions if not properly contained.

2. Material Flow Issues: Challenges like bridging, rat-holing, segregation, flow rate fluctuations and flow stagnation can disrupt smooth flow and lead to operational inefficiencies.

3. Environmental Sensitivity: Powders can be sensitive to moisture absorption and temperature fluctuations, which can alter their properties and affect handling processes.

4. Safety Concerns: Combustible powders require stringent safety measures to prevent potential explosions and accidents during handling and transportation.

Components of powder handling system design
Efficient powder handling relies on a combination of specialized equipment:
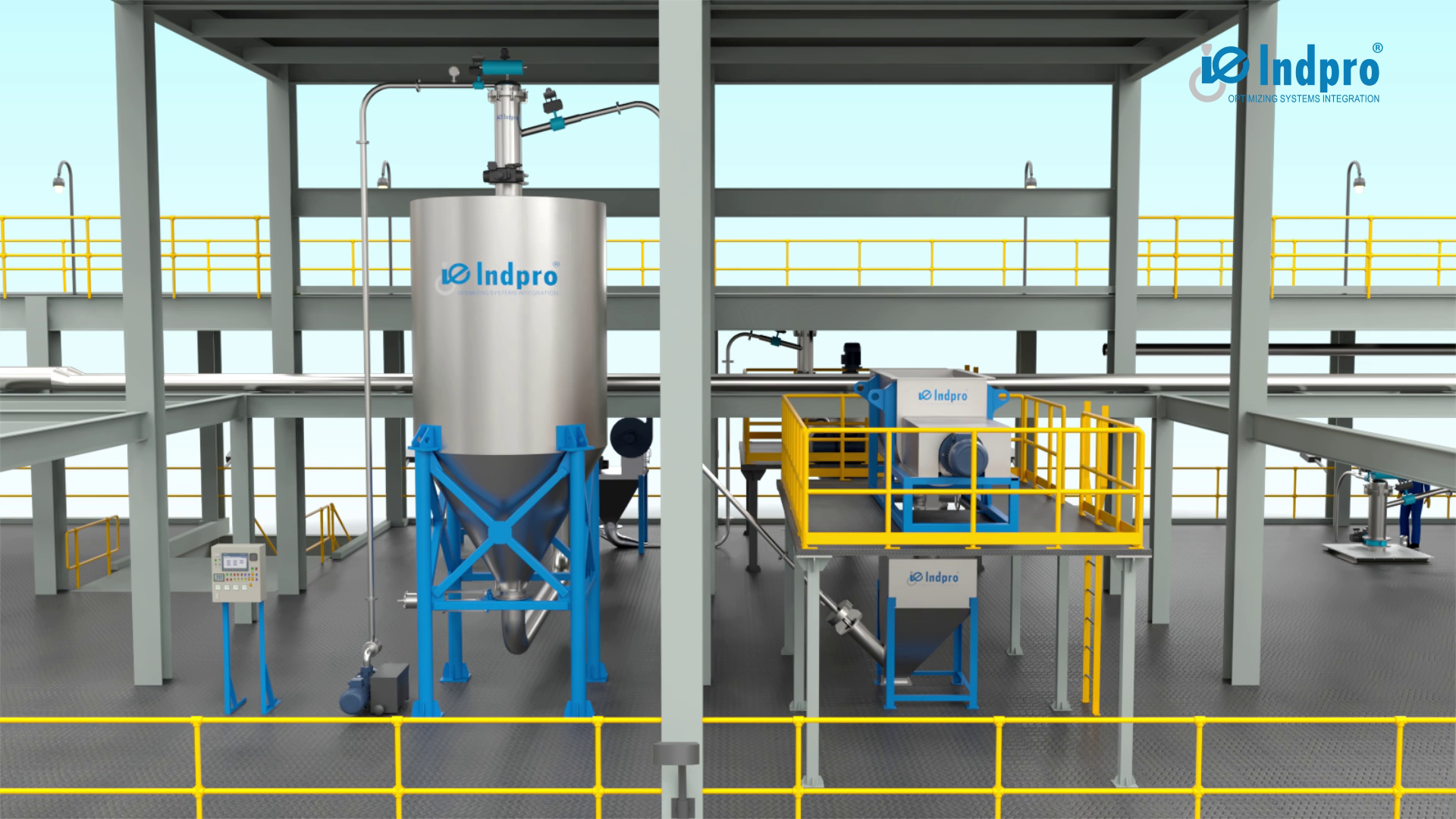
1. Storage and Feeding Equipment
- Silos and Hoppers: These are essential for bulk storage of powders. Silos are used for large-scale storage, while hoppers facilitate controlled dispensing of materials into the system. Both must be designed to minimize clogging and allow for smooth flow.

- Material Unloading Stations: Used to transfer powders from small and big bags as well as drums into the system. Equipped with dust collection systems, they ensure safe and clean handling. They come with integrated sieving systems to separate out any unwanted oversize particles and contaminants.

2. Conveying Systems
- Pneumatic Conveyors: Pneumatic powder transfer systems use air pressure or vacuum to transport fine powders through pipelines. These systems are designed to ensure efficient, dust-free operations while maintaining product integrity, making them ideal for industries with high hygiene and safety standards.
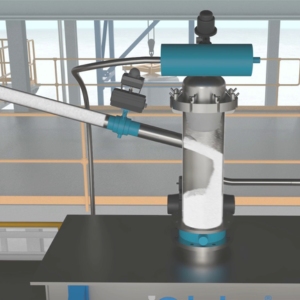
- Mechanical Conveyors: Including flexible screw conveyors, belt conveyors, and tubular screw conveyors, tube chain conveyors these are often used for short distances or heavy-duty applications.

3. Mixing and Blending Equipment:
Mixing and blending equipment are crucial for achieving homogeneity in powder processing. These systems ensure that ingredients are evenly distributed, enhancing the quality and consistency of the final product. Key types include:
- Ribbon Blenders: Designed with helical ribbon blades that move powders in opposite directions, achieving thorough mixing with minimal energy consumption.

- Paddle Mixers: Gently move materials with wide, flat paddles to maintain the integrity of fragile particles.

4. Powder Size Manipulation Equipment:
Powder size can either involve breaking down of lumps or separating out undesirable powder particle sizes.
- Lump Breakers: Reduce large lumps of materials into smaller, more manageable sizes, ensuring smooth processing and consistent material flow with minimal risk of blockages.

- Vibratory Sieves: Ensure powders meet exact particle size specifications by efficiently removing oversized particles.

5. Powder Bridge Breaking Equipment:
These devices are designed to break down powder bridges, which are solid formations that can occur within hoppers or silos, obstructing material flow. Common methods of bridge breaking include:
- Powder Bridge Breakers (iRotocon): iRotoCon is designed to avoid powder bridging in hoppers and silos due to it’s special rotary blade design. As well as preventing powder bridging, iRotoCon also provides a controlled, reliable rate of discharge.

- Vibration and Agitation: Applying vibrations or agitation to the hopper or silo walls helps dislodge powder bridges.

- Air Fluidization: Introducing a controlled flow of air into the hopper or silo helps fluidize the powder and prevent bridge formation.
- Bin Activator: This device consists of a conical top design which vibrates & breaks bridges & prevents ratholing inside silos.
Types of Handling Systems
These systems can be categorized based on their level of automation:
- Manual Systems: Suitable for small-scale operations with limited production needs.
- Semi-Automated Systems: Ideal for medium-scale processes requiring moderate control.
- Fully Automated Systems: Designed for high-volume industries with stringent precision and efficiency demands.
Key Considerations for Efficient Powder Handling
To ensure optimal performance, consider the following factors:
- Material Characteristics: Analyze the properties of powders to design an efficient handling system. Particle size determines how easily the powder flows, bulk density affects storage and conveying capacity, and flowability influences equipment selection and system performance. Understanding these characteristics ensures smoother operation and minimizes blockages.
- System Design: When designing powder conveying system, it’s essential to prevent bottlenecks that disrupt material flow and reduce efficiency. Ensure that equipment like conveyors, hoppers, and feeders are properly sized to handle the material volume without clogging. Design the system with clear, unobstructed paths, minimizing turns or complex routes that could cause slowdowns. Reduce the risk of blockages by avoiding excessive handling of powders. Utilize gravity-driven or pneumatic powder conveying systems to minimize mechanical interaction with the material.
- Hygiene Requirements: powder processing in food, pharmaceutical, and other regulated industries must meet strict hygiene standards to ensure product safety and quality. Key considerations include using non-corrosive, easy-to-clean materials like stainless steel for all components in contact with powders. Systems should be designed with smooth, non-porous surfaces and quick-disconnect fittings for easy sanitization between batches.
- Operational Costs: Invest in energy-efficient systems and implement automated control for cost reduction.
Advanced Technologies in Powder Handling
The industry is embracing innovative solutions to enhance performance:
- Automated Systems: PLCs and SCADA enable precise monitoring and control.
- Dust-Free Systems: Advanced dust collection technologies minimize environmental and health risks.
- IoT-Enabled Sensors: Real-time monitoring improves efficiency and predictive maintenance.
- Flexible Systems: Modular designs adapt to diverse powder types and processes.
Applications of Powdered Material handling System
Powder handling systems play a crucial role across various industries:
- Food Industry: Transporting and processing ingredients like flour, sugar, spices, and additives.
- Plastics & Polymer: Handling powdered resins and additives for production processes.
- Minerals: Facilitating the transportation and processing of minerals and ores.
- Pharmaceuticals: Ensuring precision in mixing powders and encapsulating ingredients for medicines.
- Chemical Industry: Safely managing reactive and hazardous powders.
- Construction: Efficiently handling materials like cement, gypsum, and fly ash.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance ensures the longevity and reliability of these material handling systems:
- Regular Cleaning: Prevent cross-contamination and maintain hygiene standards.
- Preventive Maintenance: Address wear and tear before major failures occur.
- Troubleshooting Common Issues: Resolve clogging, flow irregularities, and equipment malfunctions promptly.
Indpro's Expertise in Powder Handling
Indpro is a leading powder-handling solution provider, we offer innovative solutions to diverse markets. Our powder transfer systems & other powder handling equipment’s prioritize efficiency, safety, and reliability, backed by cutting-edge technology and years of expertise. Indpro is not just a provider of innovative powder handling solutions; we are also a leader in advanced testing and technical expertise. Our state-of-the-art Test Lab and Technical Centre are equipped with various types of tests required to develop a solution for you. Get in touch with us to learn more about how we can help you.
Efficient powder handling systems are the backbone of modern industries, ensuring productivity, quality, and safety. To achieve long-term success and seamless operations, it is crucial to invest in the right equipment and technologies. Contact experts today to revolutionize your powder handling processes.



