Battery Recycling Process of Lead-Acid and Lithium-Ion
Battery Recycling Process
In contemporary times, numerous types of equipment operate on either batteries or gas. The shared characteristic between these two elements is their finite usage; once depleted, the customary practice involves refilling gas or disposing of used batteries and acquiring replacements.
Nevertheless, discarding batteries can contribute significantly to environmental waste, given their widespread use and the presence of harmful materials within them. Consequently, disposing of batteries may not be a prudent course of action. An alternative to discarding used batteries is recycling them.
In contrast to materials like plastic and paper, battery recycling may not be as widely understood. Therefore, we’ve compiled this article to provide you with a fundamental understanding of battery recycling.

What is battery recycling?
Battery recycling is a vital practice that involves the reuse and reprocessing of batteries, with the primary objective of reducing the volume of batteries being discarded as material waste. Batteries contain a range of hazardous chemicals and heavy metals, and their improper disposal has raised significant environmental concerns, including the contamination of water and soil. Therefore, battery recycling is essential to align with environmental and health regulations, as well as to reap associated benefits.
Batteries, by their nature, have a finite lifespan. Eventually, they either become damaged or cease to function. This is precisely when battery recycling becomes crucial.
How the batteries are recycled?
It is important to understand the process of recycling batteries. There are various types of technologies and material used to produce batteries which must be considered before delving into the recycling process.
Batteries exhibit variations based on their constituent components, which encompass lead-acid, lithium-ion (Li-ion), nickel-metal hydride (Ni-MH), nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd), lithium-ion polymer, nickel-zinc, and alkaline materials. Manufacturers utilize these components to create various types of batteries, each potentially differing in terms of their intended applications, power output, and the specific recycling processes they entail.
Recycling process of Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries hold the distinction of being the earliest form of rechargeable batteries worldwide. They are composed of a combination of lead and sulfuric acid.
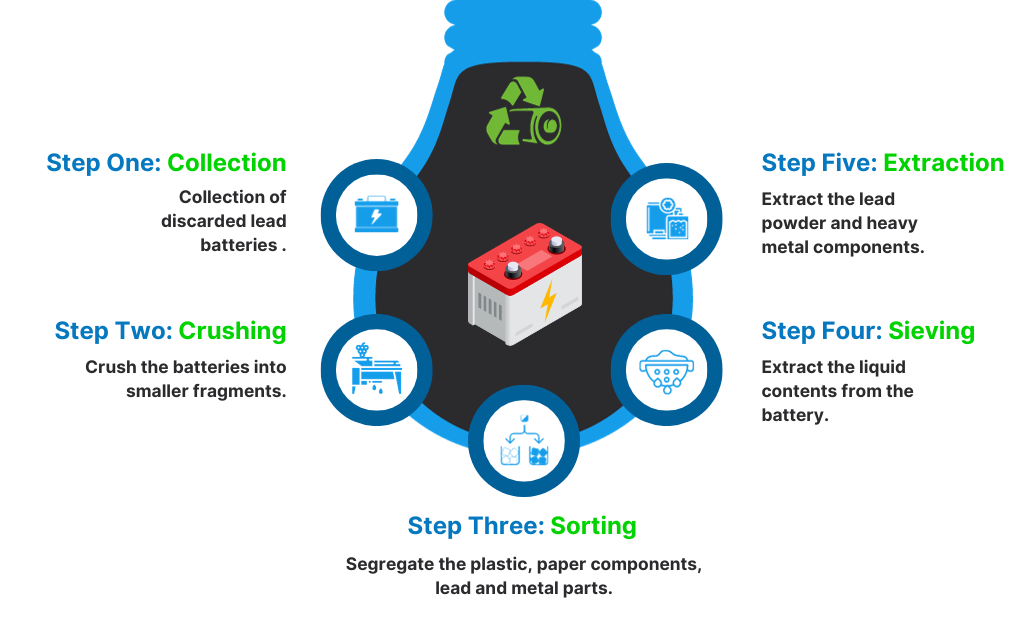
1. Collection:
The initial step in the battery recycling process entails the collection of discarded lead batteries from various disposal points.
2. Crushing :
Following the collection phase, the subsequent step in the recycling of lead batteries involves their disassembly. Recycling facilities employ mills or industrial crushers to crush the batteries into smaller fragments during this phase.
After crushing, the material is stored in small bags, jumbo bags, or in some permanent storage unit and then it is transferred to the sorting station. Automation solutions can include bag filling machine, big bag unloading station, bag dump station, and pneumatic conveying system for the crushed material to be conveyed to multiple storage silos for storing, and then as per the requirement, it can extract from those silos.
3. Sorting:
In this phase, the lead-acid battery components are meticulously separated. Recyclers distinguish and segregate the plastic and paper components from the lead and metal parts of the battery. The lead and heavy metals extracted from the battery then undergo subsequent processing for recycling.
4. Sieving:
Within this process, recyclers carry out the removal of thermoplastic components present in the battery. Following this, they utilize a sieving process to extract the liquid contents from the battery, leaving behind the dry lead components. Subsequently, the lead and heavy metals proceed to the final stage of the recycling process.
After the sieving operation, dry lead which is in powder form is passed through a cyclone separator to discharge the powder material into the collection unit which is further connected to the extraction process. Automation systems include a cyclone separator & dust collection system which will smoothly carry out the operation for feeding material into the collection unit and the generated dust shall be transferred to the centralized dust collection unit.
The scrap plastic materials from batteries are collected in the warehouse in a loose form and then they get transferred to the washing lines using a pneumatic conveying system for the extraction process. These reprocessed thermoplastics are used to create battery casings and other new plastic products by manufacturers.
5. Extraction:
In the last phase of lead-acid battery recycling, recyclers extract the lead powder and heavy metal components from the remaining battery remnants.
This procedure can be executed in two distinct manners:
Pyrometallurgy based – Pyrometallurgy is a metallurgical process that relies on heat for the extraction and purification of metals. It involves roasting, smelting and refining.
Hydrometallurgy based – Hydrometallurgy is the method employed for extracting metals from ore. It involves leaching, solution-based concentration, and purification & metal recovery.
Both hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy ultimately yield molten lead as the end product. Recyclers then shape this molten lead and deliver it to manufacturers to be used in the production of new batteries.
Recycling process of Alkaline Zinc Air /Zinc Carbon Batteries
Recycling alkaline batteries involves a mechanical dismantling process. Similar to other types of batteries, the initial step is the collection of used alkaline batteries. Subsequently, the batteries are sorted after being dismantled.
Following the disassembly of alkaline batteries, recyclers extract three key components for additional processing: steel components, plastic and paper components, and zinc and manganese components.
Subsequently, these materials are packed & sent to recycling facilities, where manufacturers recover them for the production of new products.
Recycling process of Lithium Ion, Nickel Metal Hydride, Nickel-Cadmium Batteries
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, commonly employed in cars and electronic devices, are rechargeable. Nickel-based batteries, another rechargeable type, find use in portable devices such as cameras and in home or office UPS devices.
Both lithium-ion (Li-ion) and nickel-based batteries share similarities with lead-acid batteries in the final stages of recycling. Here is a detailed step-by-step process for recycling lithium and nickel batteries.
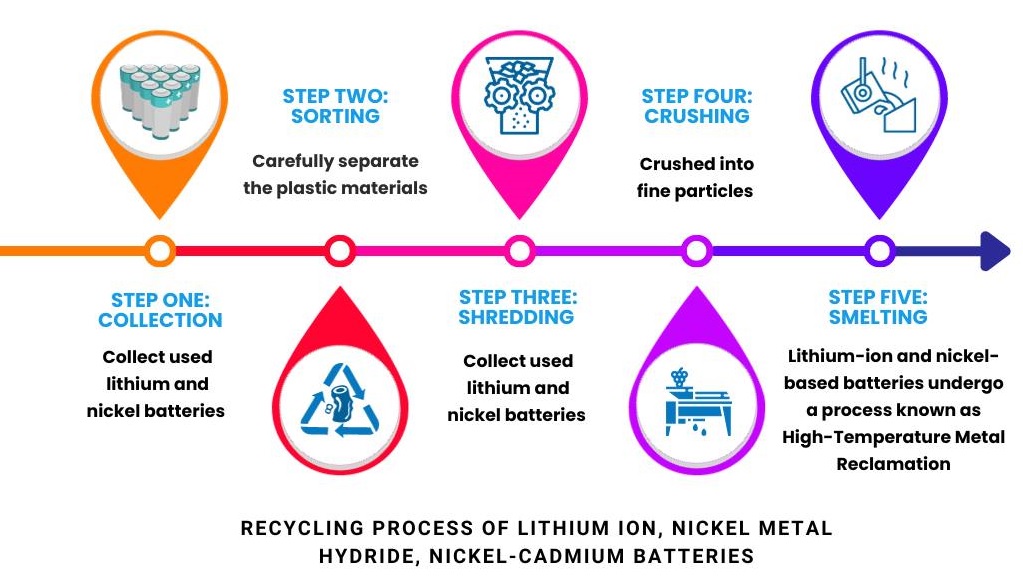
Step 1: Collection
Recyclers collect used lithium and nickel batteries from collection points or various other locations.
Step 2: Sorting
During this phase, recyclers carefully separate the plastic materials within the battery from the metal components. Both of these materials can be effectively repurposed in the creation of new products.
Step 3: Shredding
The sorted batteries are passed through a shredder which breaks the battery into coarse particles. After shredding, the coarse material is then transferred to the crushing station using a conveying system.
Step 5: Smelting
In this phase, the components of lithium-ion and nickel-based batteries undergo a process known as High-Temperature Metal Reclamation. During this process, metals present in the batteries, such as nickel, manganese, chromium, and iron, are extracted, conveyed via line to packaging station & and sent to manufacture new products.
Step 4: Crushing
The different types of shredded materials are then crushed into fine particles by using a mill or crusher, and collected material gets conveyed using a conveying system to the smelting process.
Recycling process of Mercury Batteries
Mercury batteries, after collection, undergo recycling through liquid and heat extraction methods. These batteries contain highly toxic heavy metals, necessitating their processing in carefully controlled extraction environments to minimize environmental and health risks.
The mercury obtained through these extraction processes serves as a valuable resource for manufacturing new mercury batteries, measuring instruments, and components for fluorescent lights. Additionally, manufacturers can repurpose the plastic and other materials obtained from the batteries to create various new products.
Benefits of battery recycling
- Conservation of Non-Renewable Resources
- Prevents pollution
- Minimizes solid waste deposited in landfills
- Energy saving



