Common Super Sack Unloader Problems
Common Super Sack Unloader Problems
and How to Address Them
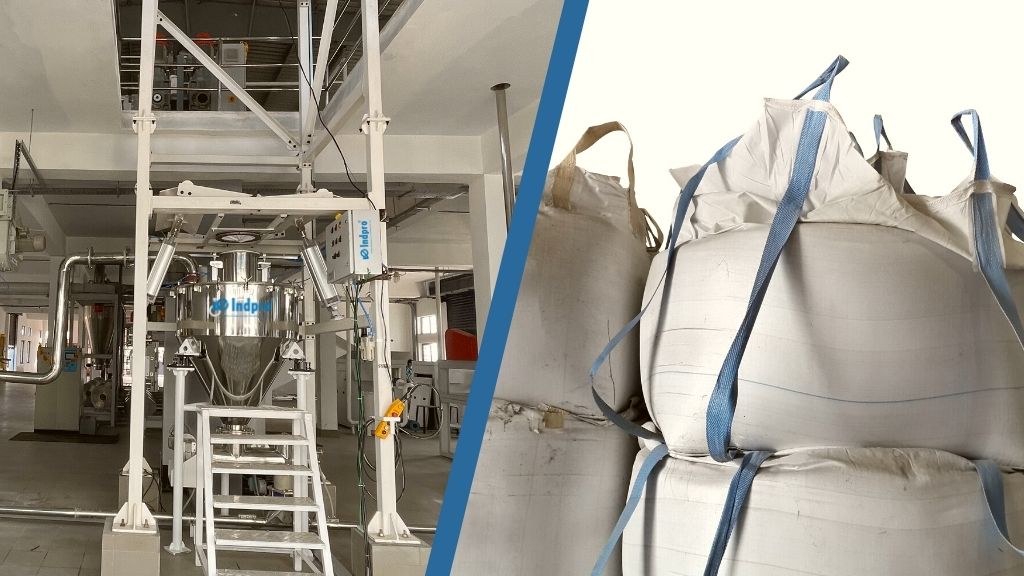
Super sack unloaders, also known as bulk bag unloaders or big bag unloading system, are essential equipment in various industries for efficiently transferring and discharging bulk materials from flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs), commonly referred to as super sacks or jumbo bags. However, like any machinery, super sack unloaders can experience issues that might hinder their performance and efficiency. In this blog, we will explore some of the most common problems associated with super sack discharging and provide insights into how to address them.

1. Material Flow Issues:
Causes: Material bridging, compacting, or improper flow properties.
Solution:
- Utilize massaging plates to promote material flow.
- Ensure proper storage and handling of materials to prevent compaction.
- Select super sack unloaders with features designed to tackle challenging flow properties.
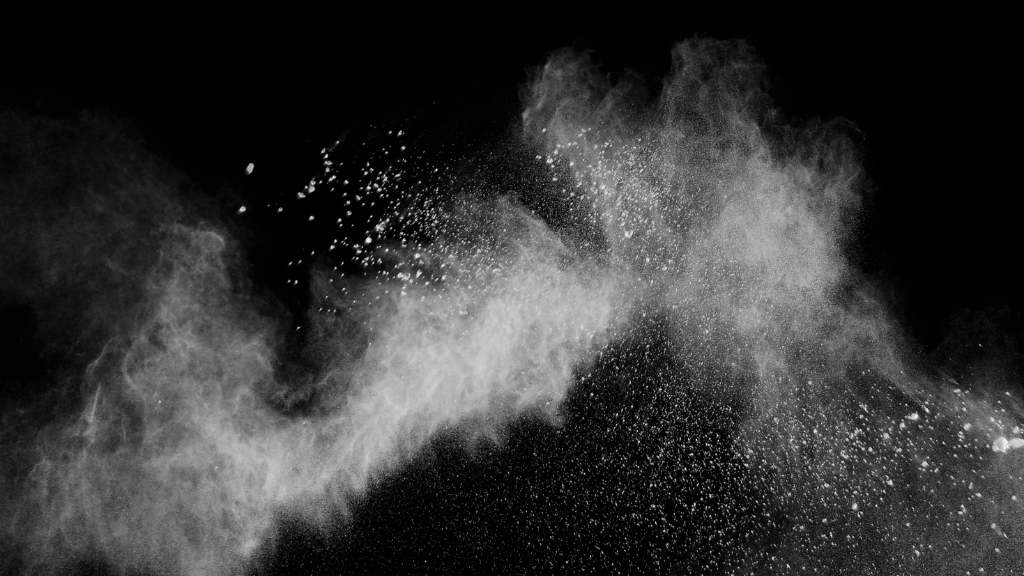


2. Dust Emission and Contamination:
Causes: Inadequate dust containment systems, poor sealing, or improper handling of dusty materials.
Solution:
- Install efficient dust collection and containment systems, such as dust collectors and hoods.
- Choose super sack discharger with integrated dust control features.
- Use super sacks with spout liners to prevent material leakage.
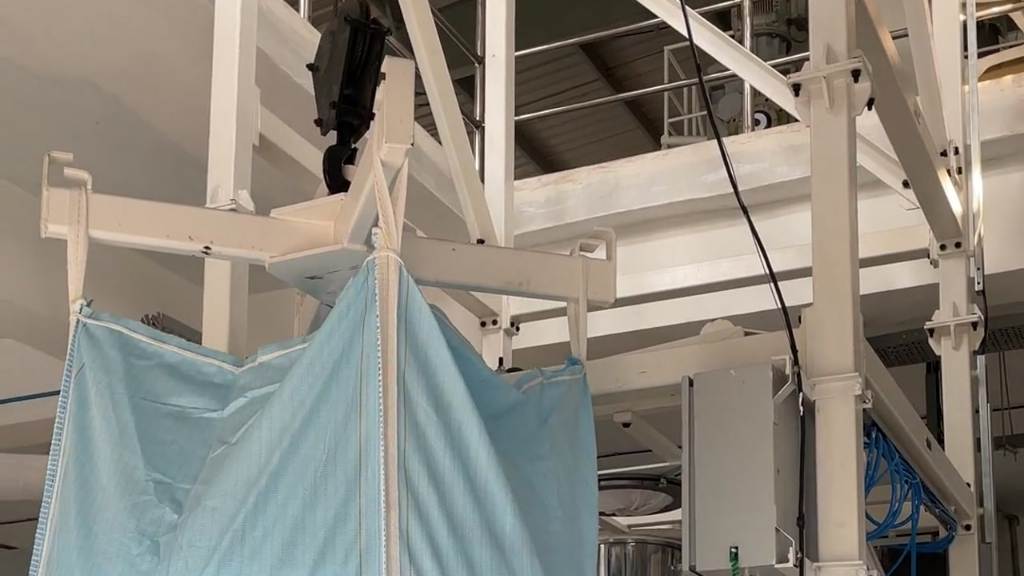
3. Incomplete Discharge:
Causes: Improper positioning of the super sack, discharge chute blockage, bag massager not installed or inefficient unloading mechanisms.
Solution:
- Opt for super sack unloaders with features like electro-pneumatic operated massaging plates to help massage and discharge difficult to flow products.
- Ensure the super sack is positioned correctly and hanging freely to allow complete discharge.
- Regularly inspect and clear any blockages in the discharge chute.
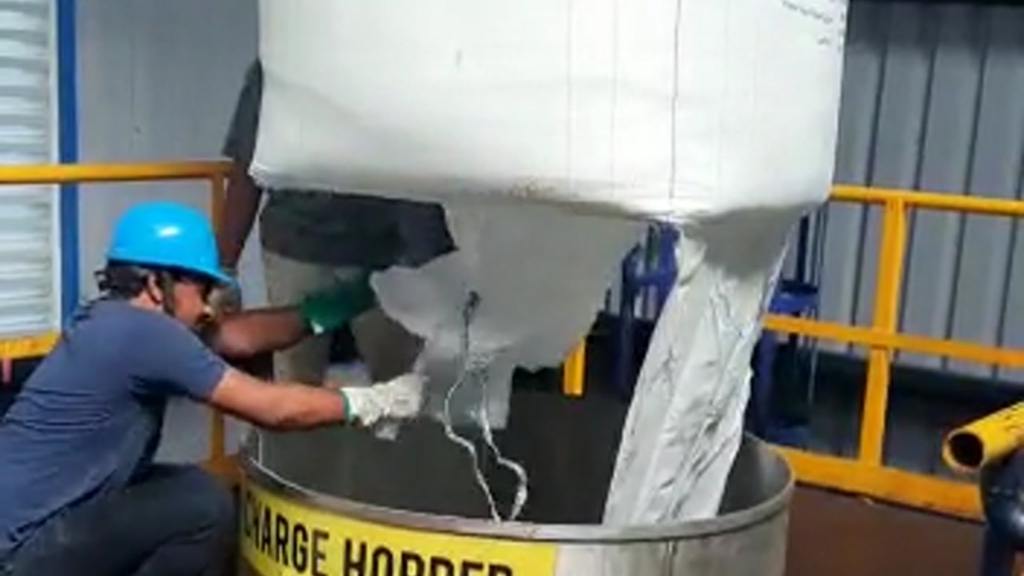


4. Equipment Jamming or Overloading:
Causes: Overloading the unloader beyond its capacity, foreign objects in the equipment, or mechanical issues.
Solution:
- Adhere to the recommended weight capacity of the super sack unloader.
- Implement proper quality control measures to prevent foreign objects from entering the equipment.
- Regular maintenance and inspection of mechanical components to prevent breakdowns.
5. Operator Safety Concerns:
Causes: Inadequate safety features, lack of operator training, or improper handling of equipment.
Solution:
- Prioritize safety by choosing super sack unloaders with built-in safety features like interlocks and guarding.
- Provide thorough training to operators on proper handling and safety procedures.
- Regularly inspect equipment for potential safety hazards.


6. Mechanical Failures:
Causes: Wear and tear, lack of maintenance, or manufacturing defects.
Solution:
- Establish a routine maintenance schedule and conduct regular inspections.
- Address any signs of wear or malfunction promptly to prevent larger issues.
- Work closely with the equipment manufacturer for technical support and replacement parts.
Super sack unloaders are indispensable tools for efficient bulk material handling, but they can encounter various challenges that hinder their optimal performance. By understanding and addressing these common problems, industries can ensure the smooth operation of their bulk bag dischargers, enhance productivity, and maintain a safe working environment for operators. Regular maintenance, proper handling of materials, and investing in quality equipment can go a long way in mitigating these challenges and ensuring the seamless unloading of bulk materials. Get in touch with Indpro’s experts on this subject to learn more on this subject!